What exactly is Big Data?
- Data sets so voluminous and complex that traditional data-processing application software are inadequate to deal with them.
- ”From the dawn of civilization until 2003, humankind generated five exabytes of data. Now we produce five exabytes every two days…and the pace is accelerating.” – Eric Schmidt
- Lately, the term “big data” tends to refer to the use of predictive analytics, user behavior analytics, or certain other advanced data analytics methods that extract value from data, and seldom to a particular size of data set
The Four Vs of Big Data :
Volume
- The sheer volume that that is being generated each second is what makes Big data “BIG”.
- There has been an exponential growth each year and yet we have only begun collecting data since 2000. According to Thomson Reuters, in 2010 the world was “awash with over 800 exabytes of data and growing.”
Velocity
- It is the frequency at which new data is generated and needs to be processed. Think about the millions of Tweets, SMS Messages, WhatsApp Messages, Facebook Status Updates, Instagram Posts, Credit Card Swipes are being carried out.
- This has meant the immediate need of technology which can process data as it is being generated.
Variety
- Traditionally we have been collecting structured data i.e. Bank Statements like date, amount and time. These kind of data easily fit into relational databases, however they make up only a fraction of the world’s data.
- With the advent of Social Media, structured data is augmented by unstructured data. These unstructured data comes from all possible means i.e. Social Media Platforms, Audio Files, Images, Videos, Web Pages, Log Files & etc.
Veracity
- Veracity simply refers to the trustworthiness of the data.
- Since more than 80% of the data collected are unstructured, there is less control on the quality and accuracy of such data.
- This makes it difficult to rely on the data being an accurate representative.
Who are the players using Big Data?
- Only 18% of companies believe they have the skills necessary to gather and use insights effectively.
- Only 19% of companies are confident that their insights-gathering processes contribute directly to sales effectiveness. (source: McKinsey)
Simply collecting data does not unleash its business effectiveness. Big data is a term for large volumes of data – both structured and unstructured – that inundates a business on a day-to-day basis. But it’s not the amount of data that’s important. It’s what organizations do with the data that matters.
Where is Big Data used?
When you think of “big data”, for many, it’s a nebulous term that invokes images of huge server farms humming away. Or perhaps you think of receiving some kind of personalized advertisement from a retailer. But big data is so much deeper and broader than that. Here are 10 prominent ways :
- Understanding and Targeting Customers – This is one of the biggest and most publicized areas of big data use today. Here, big data is used to better understand customers and their behaviors and preferences. Companies are keen to expand their traditional data sets with social media data, browser logs as well as text analytics and sensor data to get a more complete picture of their customers. The big objective, in – many cases, is to create predictive models.
- Understanding and Optimizing Business Processes – Big data is also increasingly used to optimise business processes. Retailers are able to optimise their stock based on predictions generated from social media data, web search trends and weather forecasts.
- Personal Quantification and Performance Optimisation – Big data is not just for companies and governments but also for all of us individually. We can now benefit from the data generated from wearable devices such as smart watches or smart bracelets. Take the Up band from Jawbone as an example: the armband collects data on our calorie consumption, activity levels, and our sleep patterns. While it gives individuals rich insights, the real value is in analysing the collective data.
- Improving Healthcare and Public Health – The computing power of big data analytics enables us to decode entire DNA strings in minutes and will allow us to find new cures and better understand and predict disease patterns. Just think of what happens when all the individual data from smart watches and wearable devices can be used to apply it to millions of people and their various diseases. The clinical trials of the future won’t be limited by small sample sizes but could potentially include everyone!
- Improving Sports Performance – Most elite sports have now embraced big data analytics. We have the IBM SlamTracker tool for tennis tournaments; we use video analytics that track the performance of every player in a football or baseball game, and sensor technology in sports equipment such as basket balls or golf clubs allows us to get feedback (via smart phones and cloud servers) on our game and how to improve it. Many elite sports teams also track athletes outside of the sporting environment – using smart technology to track nutrition and sleep, as well as social media conversations to monitor emotional well-being.
- Improving Science and Research – Science and research is currently being transformed by the new possibilities big data brings. Take, for example, CERN, the nuclear physics lab with its Large Hadron Collider, the world’s largest and most powerful particle accelerator. Experiments to unlock the secrets of our universe – how it started and works – generate huge amounts of data.The CERN data center has 65,000 processors to analyse its 30 petabytes of data. However, it uses the computing powers of thousands of computers distributed across 150 data centers worldwide to analyse the data. Such computing powers can be leveraged to transform so many other areas of science and research.
- Optimising Machine and Device Performance – Big data analytics help machines and devices become smarter and more autonomous. For example, big data tools are used to operate Google’s self-driving car. The Toyota Prius is fitted with cameras, GPS as well as powerful computers and sensors to safely drive on the road without the intervention of human beings. We can even use big data tools to optimize the performance of computers and data warehouses.
- Improving Security and Law Enforcement – Big data is applied heavily in improving security and enabling law enforcement. I am sure you are aware of the revelations that the National Security Agency (NSA) in the U.S. uses big data analytics to foil terrorist plots (and maybe spy on us). Others use big data techniques to detect and prevent cyber attacks. Police forces use big data tools to catch criminals and even predict criminal activity and credit card companies use big data use it to detect fraudulent transactions.
- Improving and Optimizing Cities and Countries – Big data is used to improve many aspects of our cities and countries. For example, it allows cities to optimize traffic flows based on real time traffic information as well as social media and weather data. A number of cities are currently piloting big data analytics with the aim of turning themselves into Smart Cities, where the transport infrastructure and utility processes are all joined up. Where a bus would wait for a delayed train and where traffic signals predict traffic volumes and operate to minimize jams.
- Financial Trading – The final category of big data application comes from financial trading. High-Frequency Trading (HFT) is an area where big data finds a lot of use today. Here, big data algorithms are used to make trading decisions. Today, the majority of equity trading now takes place via data algorithms that increasingly take into account signals from social media networks and news websites to make, buy and sell decisions in split seconds
Big Data and IoT in Smart Farming :
What is Smart Farming?
- Smart Farming is a development that emphasizes the use of information and communication technology in the cyber-physical farm management cycle.
- New technologies such as the Internet of Things and Cloud Computing are expected to leverage this development and introduce more robots and artificial intelligence in farming.
- This is encompassed by the phenomenon of Big Data, massive volumes of data with a wide variety that can be captured, analysed and used for decision-making.
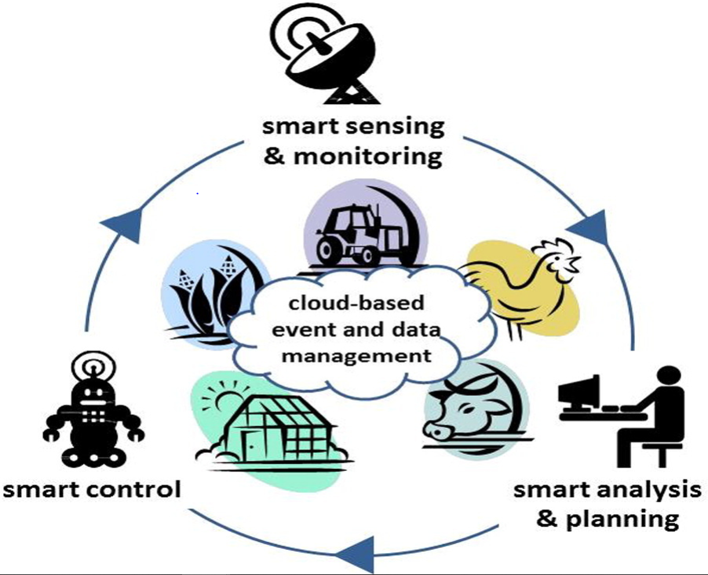
Management cycle of Smart Farming
How is Big Data and IoT being leveraged in Smart Farming?
- With the need to produce more food using fewer inputs, agriculture is seeking new products, practices and technologies.
- Big Data technologies are playing an essential, reciprocal role in farming: machines equipped with all kind of sensors that measure data in their environment are being used to increase efficiency.
- Starting with the vastly increased supply of information everywhere from the plant genome to water management, fertilization, climate, soil, machinery, and crop protection systems. Farmers are expanding ways to get and use data both in both farming practices and advances in crop genetics.
- Let us look at a few examples below
1 : Department of Agricultural Extension (DOAE), Thailand
- Department of Agricultural Extension (DOAE) and its partners have launched a one-year pilot project that introduces this IoT based solution to monitor, analyze and predict the factors affecting cultivation.
- The new solution will allow farmers to have access to a more precise farming system that helps increase crop yields, control quality of agricultural products and reduce production costs.
- The benefits have been so good that many countries are looking to adopt IoT based solutions to collect big data and utilize it in a meaningful way
2 : Vodafone, New-Zealand
- Vodafone’s Precision Farming solution in New Zealand allows farmers to use only the amount of fertilizer they need.
- A special GPS Farming device is installed in the vehicle spreading the fertilizer and data is sent via Vodafone’s network to Precision Farming’s secure server.
- This data is then overlaid on a computerized map, so the farmer can login and see where every last kilogram has been deposited. With accurate feedback from their fertilizer program, farmers can instantly spot any wastage and adjust their next order.
- Vodafone’s Precision Farming system relies on GPS and machine-to-machine technology. The operator supplies the special SIMs required, and the Precision Farming system is linked to Vodafone’s network to ensure continuous transmission of data from the field.
- The system provides constant monitoring of the width and rate of fertilizer application, so farmers can check the virtual trail left by the fertilizer spreader and fine-tune their farm management accordingly.
- The precision agriculture system can be applied to other activities, such as spraying and effluent spreading, to ensure farmers get optimum results from all substances applied to the land.
3 : Libelium Technology in Colombia
- In Colombia, local organization Red Tecnoparque Colombia has deployed a wireless sensors network with Libelium technology to monitor crops in Lembo area, in Santa Rosa de Cabal region.
- Red Tecnoparque Colombia has selected Spanish firm Libelium’s Waspmote Plug & Sense! Sensor Platform to develop a precision agriculture project with remote sensors. Plantain crops have been monitored with different sensors added to Waspmote Plug & Sense!
- Libelium’s sensors allow producers to monitor key parameters including humidity, temperature, soil moisture, soil temperature, trunk diameter, fruit diameter, pluviometer and solar radiation.
- Through the monitoring of these parameters, Redcom Tecnoparque can remotely supervise ambient and agronomic variations to investigate new banana varieties. This solution also lets them to know harvesting projection, to optimize water usage, to prevent plagues and diseases, to reduce fertilizers consumption and to classify soils.